Michael Porter was one of the best business thinkers during the last decades. He is the author of 18 business books and more than 130 articles in the prestigious Harvard Business Review. He taught his business skills all over the world to governments, top global companies, organizations and academics business schools.
Porter developed a famous business model called the “five forces of competition”. This strategy assists companies to find out more about their core business and so to generate a profitable market. Therefore, he identified 5 competitive forces, such as:
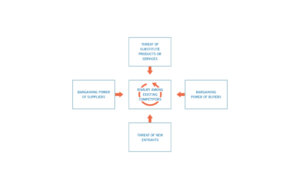
Source: The Five forces concept
https://www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/business-strategy/Pages/the-five-forces.aspx
- The Suppliers’ bargaining power is high if the market is dominated by a few large suppliers plus their customers are fragmented and weak. For instance, oil is a scarce resource and is dominated by a few countries.
- The Buyers’ bargaining power is high if the market is dominated by a few large buyers and they buy in large quantity. In the food industry, distributors and supermarket chains have a high bargaining power.
- Competitive rivalry between existing players: Competitors. The force of rivalry is as its peak when growth in the industry is slow, customer loyalty is low, and products are not differentiated from the competitors.
- The threat of New entrants is high when the cost of entering the market is low. To limit access to new entrants and protect their markets, firms have to possess patents or high protocols, develop their brand reputation and invest largely in the research and development, such as in the pharmaceutical (Sanofi), airlines (Emirates) or IT (Microsoft) industries.
- The threat of Substitute products or services is low if there are barriers to enter the market. Indeed, patents, proprietary knowledge, government regulation and scarce resources will deter new entrants to compete.
Moreover, Michael Porter developed his generic business strategies diagram, as follow:
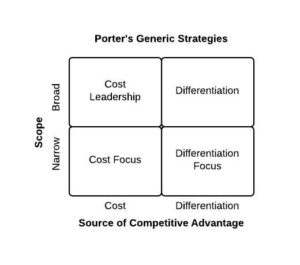
Source: Porter generic strategies
https://www.enotesmba.com/2013/05/marketing-notes-defining-competitive-strategy_4.html
There are two fundamental strategies to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage:
- A cost leadership strategy where the firm develops the same level of quality as its rivals but at a lower cost. This strategy is based on efficient processes, cheaper raw materials and an optimized value chain to save cost.
- A differentiation strategy where the company delivers products with unique qualities and something new and different from the competition. The clients, therefore, are willing to pay extra money to buy them. (cf. Blue ocean strategy concept – other BSNF articles).
According to Michael Porter, there may be a third strategy, called a focus strategy. Here, companies move towards a niche market to satisfy their unique customer’ needs with sometimes high value products (example: Ferrari – Focus strategy with a differentiation).
Further, I recommend the Blue Ocean Strategy and Blue Ocean Shift (beyond the competition) from Chan Kim and Renée Mauborgne which helps you to build uncontested markets rather than compete in the same markets.
Let us to elaborate on your personal strategy and future business at your offices or during a conference call. Please, visit: www.bsnf.eu and contact us by email at contact@bsnf.eu


Leave a Comments